Advanced Discussion (show/hide)»
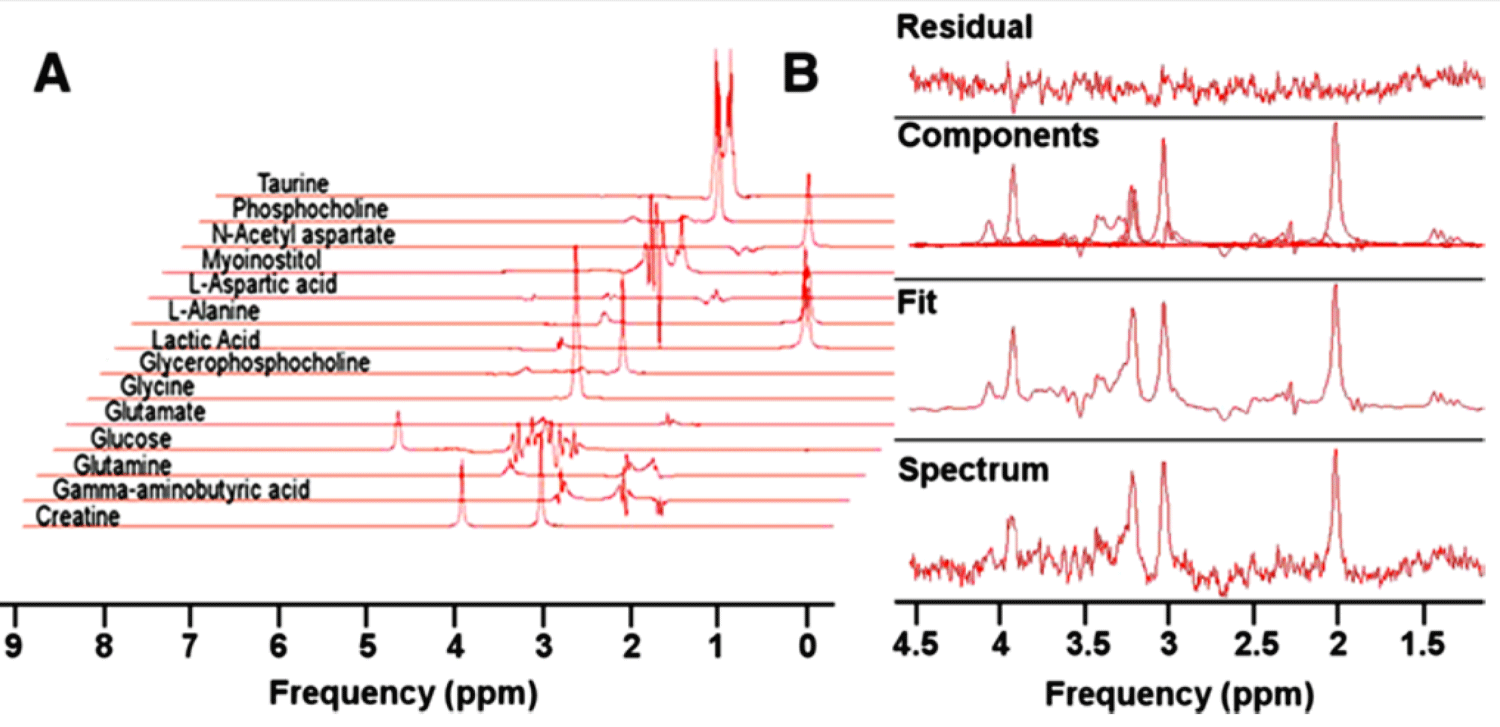
Provencher's LCModel is commercially available and has been available since the mid-1990s. LC stands for “linear combination”, producing a solution representing the sum of contributions from individual metabolite spectra of pure compounds. The technique assumes spectral features such as chemical shifts, J-coupling, spectral distortions and localization errors will be identical across the sample. Exclusions may lead to a systemic bias.
The jMRUI toolbox contains several useful MRS quantitation and processing programs, including the relatively popular AMARES (Advanced Method for Accurate, Robust, and Efficient Spectral fitting). Unlike the LCModel which does fitting in the frequency domain, AMARES performs its estimation and corrections in the time domain.
Even sophisticated curve fitting programs like LCModel and AMARES have difficulty controlling for the undulating macromolecular baseline. A separate experiment may be required to measure this baseline where large differences in T1 relaxation between metabolites and other macromolecules can be used to null the metabolites of interest.
Alger JR. Quantitative proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging of the brain: a didactic review. Top Magn Reson Imaging 2010; 21:115-128. (good recent review)
Barker PB, Soher BJ, Blackband SJ, et al. Quantitation of proton NMR spectra of the human brain using tissue water as an internal concentration reference. NMR Biomed 1993; 6:89-94.
Gasparovic C, Song T, Devier D, et al. Use of tissue water as a concentration reference for proton spectroscopic imaging. Magn Reson Med 22006; 55:1219-1226.
Jansen JFA, Backes WH, Nicolay K, Kooi ME. ¹H MR spectroscopy of the brain: absolute quantification of metabolites. Radiology 2006; 240:318-322.
Mandal PK. In vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic signal processing for the absolute quantitation of brain metabolites. Eur J Radiol 2012; 81:e653-e664. *(good review)
Poullet J-B, Sima DM, Van Huffel S. MRS signal quantitation: a review of time- and frequency-domain methods. J Magn Reson 2008; 195:134-144.
Provencher SW. Estimation of metabolite concentrations from localized in vivo proton NMR spectra. Magn Reson Med 1993;30:672-679.
Provencher S. LCModel & LCMgui User's Manual. 2016. (Complete documentation of most current software version available from this link)
Stefan D, Di Cesare F, Andrasescu A, et al. Quantitation of magnetic resonance spectroscopy signals: the jMRUI software package. Meas Sci Technol 2009; 20:1040355 (9 pp).
Vanhamme L, van den Boogaart A, Van Huffel S. Improved method for accurate and efficient quantification of MRS data with use of prior knowledge. J Magn Reson 1997; 129:35-43. (Description of AMARES method).
What causes magnetism?
